Hooke's Law Describes the Force of
None of the above. F force appliedF k force constantNm-1 xextension of spring m Force Constant.
Biomeca Understanding Elastic Properties Of The Skin
A perfectly elastic collision is a collision A.
. Hookes law is named after its creator British physicist Robert Hooke who stated in 1678 that the extension is proportional to the force The law essentially describes a linear relationship between the extension of a spring and the restoring force it gives rise to in the spring. Where k is the spring constant. Δ x is the change in the length of the spring measured from its position at rest.
F k Δ x. That is F kd where k is the measure of the stiffness of. Learn about elasticity and how to determine the force exerted by a spring.
Tensione none of the above. Also called restoring force which always points in the opposite direction of the displacement. That conserves thermal energy.
It also applies to wires under tension and concrete columns under compression. Hookes Law discovered in 1660 describes the elasticity torsion and force of springs making it extremely important when it comes to the design and use of springs for compressors. Our mission is to provide a free world-class education to anyone anywhere.
A body is elastic if it recovers its original shape or size when the applied forces. Springs are created as a result of human engineering and creativity And the best way to understand how springs work is to gain an understanding of their mechanics. What is the extension of spring D.
Hookes Law is stated mathematically as follows. Hookes law describes the force ofa. The extension of an elastic object such as a spring is described by Hookes law.
In other words it takes twice as much force to stretch or compress a spring twice as much. A mass of 050 kilogramhung vertically from this spring stretches the spring 0075 meterThe value or the force constant for the spring is most nearly 033 Nm 066 Nm 66 Nm 33 Nm 66 Nm. Hookes law describes the force of A.
If extension Stretched length - original length. HOOKES LAW Itziar Ugarte INTRODUCTION Statics is the part of mechanics that studies the conditions that must be met for a body on which forces act to remain in equilibrium. In both cases the relationship between the magnitude of force F used to stretch or compress the spring by a length Δ x is given by Hookes law as follows.
Under these conditions the object returns to its original shape and size upon removal of the load. Hookes law describes the force ofa. I am debating between a and b.
This simple experiment uses the stretching of a wire by the addition of various weights. When the elastic materials are stretched the atoms and molecules deform until stress is applied and when the stress is removed they return to their initial state. A mass of 040 is connected to the end of a horizontal spring with an elastic spring constant of 150 Nm which it is stretched by a distance of 007 m.
The value of k depends not only on the kind of elastic material under consideration but also on its dimensions and shape. 5 0 k g object is hung from the other end the length of the spring is 4 1. Under the action of an external force a body can undergo a deformation that causes it to change shape or size.
Can anyone clarify the correctresponse. Tensione none of the above. F spring -kX.
Hookes law states that the force needed to exert or compress a spring by some distance is proportional to that distance within the elastic limit. Intro to springs and Hookes law. Hookes Law describes the force needed to stretch a spring.
Up to 256 cash back An ideal spring obeys Hookes law F kx. Force F is measured in newtons N. Hookes Law one dimension describes the relationship be-tween the force applied to an unstretched spring and the amount the spring is stretched when the force is applied.
In the equation F is the force x is the. That conserves kinetic energy. B The load and the spring are taken down.
Hookes law describes a certain light spring of unstretched length 3 5. Hookes law describes the force of F -Kx Here F represents the equal and oppositely applied to restore causing the elastic materials to get back to their original dimensions. Hookes law describes how as the force increases the rate of increase of.
According to Newtons third law if a spring is stretched or compressed using force F as a reaction the. That conserves potential energy. Potential energy stored in a spring.
The spring wants to restore itself to its equilibrium or normal length. If F is force k is spring constant and x is extension Hookes Law tells us that. A spring scale works by using a spring that is stretched to measure how much force present that caused the stretch.
F kx 1 where F is the applied force exerted by the spring expressed in. Hookes law states that the strain of the material is proportional to the applied stress within the elastic limit of that material. I am debating between a and b.
F spring force in the spring N. A graph of extension against force for an elastic material is. When one end is attached to the top of a door frame and a 7.
Hookes Law states that the force F required to compress or stretch a spring within its elastic limits is proportional to the distance d that the spring is compressed or stretched from its original length. Hookes law law of elasticity discovered by the English scientist Robert Hooke in 1660 which states that for relatively small deformations of an object the displacement or size of the deformation is directly proportional to the deforming force or load. Potential energy stored in a spring.
This chapter describes an experiment that confirms Hookes law concerning elasticity which relates the force on an elastic material to its extension. Mathematically Hookes law states that the applied force F equals a constant k into the displacement or change in length x or F kx. A Find its spring constant.
Force spring constant extension F ke This is when.
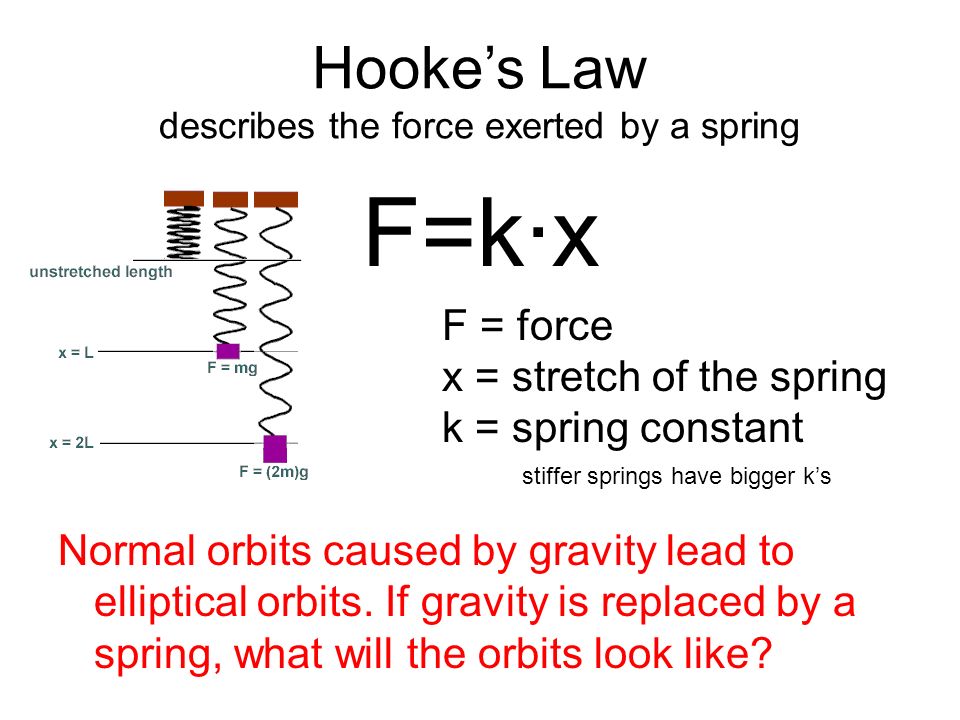
Hooke S Law Orbital Motion Reduced Gravity Flight Experiment Ppt Download

Hooke S Law Describes A Very Important Principle That Affects Many Common Daily Phenomena The Relationship Of The Force On A Spring Begin Co Math Law Physics

Hooke S Law Describes The Linear Relationship Between The Force F Or Download Scientific Diagram
No comments for "Hooke's Law Describes the Force of"
Post a Comment